GitBasicNotes
1. Git Configuration
Basic Configuration
Git needs basic configuration to work effectively. The most common settings are the user name and email, which Git uses to label commits.
# Set your name
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
# Set your email
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global user.name "spnarkhede"
git config --global user.email [email protected]
git config --global core.autocrlf false
git config --global core.editor vim
git config --global credential.helper store
git config --global color.ui true
git config --global init.defaultBranch main
git config --global push.default simple
git config --global merge.conflictstyle diff3
git config --global pull.rebase true
git config --global rebase.autoStash true
git config --global alias.s "status"
git config --global alias.c "commit --verbose"
git config --global alias.a "add"
git config --global alias.rs "restore --staged"
git config --global alias.st "stash"
git config --global alias.pr "pull --rebase"
git config --global alias.rpo "remote prune origin"
git config --global commit.template $HOME/.gitmsg.md
git config --global commit.gpgsign true
git config --global gpg.program gpg
git config --global user.signingkey <pub-keyID>
# after 1s, git auto correct wrong command
git config --global help.autocorrect 10
Proxy Configuration
If you're behind a proxy, you can configure Git to use it:
# Set HTTP proxy
git config --global http.proxy http://proxy.example.com:8080
# Set HTTPS proxy
git config --global https.proxy https://proxy.example.com:8080
# Remove proxy
git config --global --unset http.proxy
git config --global --unset https.proxy
# GitHub proxy.
git config --global url."https:/hub.fastgit.org/".insteadOf "https://github.com/"
# Socks5 proxy.
git config --global http.proxy 'socks5://127.0.0.1:1080'
git config --global https.proxy 'socks5://127.0.0.1:1080'
# Post buffer configuration.
git config --global http.postbuffer 524288000
git config --global https.postbuffer 1048576000
List and Help
You can list all the Git configurations with:
git config --list
For help with any Git command:
git help <command>
git config --list
git --help
man git-
git help
git help config
Git Ignore File
A .gitignore file tells Git which files or directories to ignore in a project.
Example .gitignore for a Node.js project:
node_modules/
.DS_Store
.env
Add .gitignore to your repository:
git add .gitignore
git commit -m "Add .gitignore"
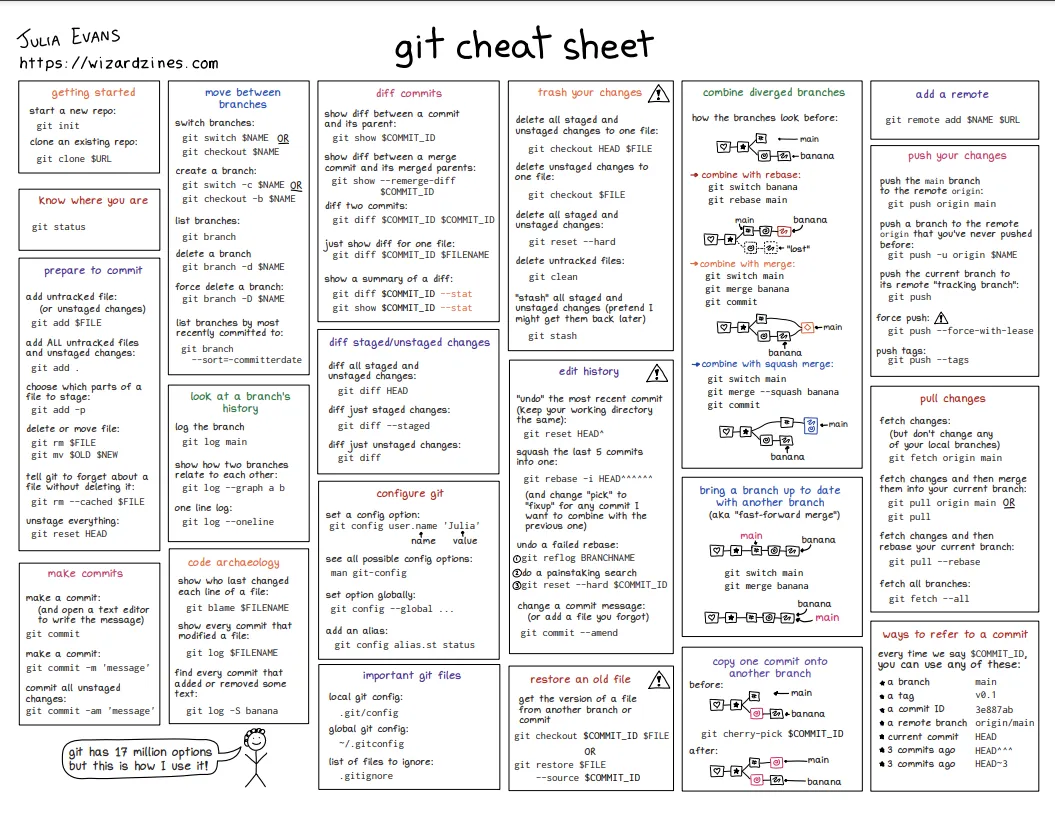
2. Git Operations
Add
Adds changes to the staging area before committing:
git add <file>
git add .
Remove
Removes files from the working directory and the index:
git rm <file>
Move
Moves or renames a file:
git mv <old-name> <new-name>
Clean
Cleans up untracked files in your working directory:
git clean -fd
Commit
Commits the staged changes:
git commit -m "Your commit message"
Commit Style Guide
Follow these guidelines for commit messages:
- Use the imperative mood ("Fix bug", not "Fixed bug").
- Be concise yet descriptive.
- Keep lines under 72 characters.
- Capitalize the first letter of the message.
Git Commit Tool
Use the interactive commit tool:
git commit --amend
Git Commit Emoji
Use emojis for clearer commit messages. Some common examples:
- 🐛 for bug fixes
- ✨ for new features
- 📝 for documentation updates
To enable Git commit emojis, you can use a tool like gitmoji-cli.
Stash
Temporarily saves changes without committing:
git stash
git stash pop
Revert
Reverts a commit by creating a new commit that undoes the changes:
git revert <commit-id>
Reset
Resets your working directory and staging area to a previous state:
git reset --hard <commit-id>
Log
Shows the commit history:
git log
Pretty Format
You can format the log output:
git log --oneline
git log --graph --oneline --decorate --all
Log Options
You can filter the log output:
git log --since="2 weeks ago"
git log --author="John Doe"
Log Filter
To show logs for specific files:
git log <file-name>
Reflog
Shows the history of the HEAD and updates:
git reflog
Show
Shows the content of a commit or branch:
git show <commit-id>
Alias
Create shortcuts for Git commands:
git config --global alias.co checkout
git config --global alias.br branch
git config --global alias.ci commit
3. Remote Operations
Remote
Add a remote repository:
git remote add origin https://github.com/username/repository.git
Pull
Fetch and merge changes from the remote repository:
git pull origin main
Fetch
Fetch updates from the remote without merging:
git fetch origin
Merge
Merge changes from one branch into another:
git merge <branch-name>
Rebase
Rebase your branch onto another:
git rebase <branch-name>
Push
Push local commits to the remote repository:
git push origin <branch-name>
4. Branching
Basic Branch Workflow
-
Create a new branch:
git branch <branch-name> -
Switch to the branch:
git checkout <branch-name> -
Merge the branch:
git merge <branch-name> -
Delete the branch after merging:
git branch -d <branch-name>
Advanced Branch Workflow
-
Create and switch to a new branch in one step:
git checkout -b <branch-name> -
Rebase a branch onto another:
git rebase <base-branch>
Tag
Tags are useful for marking specific commits:
git tag v1.0.0
git push origin v1.0.0
5. Submodule
Git submodules are repositories inside another repository:
git submodule add <repository-url> <path-to-submodule>
git submodule update --init --recursive
6. Diff and Patch
Diff
Shows the difference between changes:
git diff
Patch
Generates a patch from the diff:
git diff > patch.diff
7. Bisect
Used to find the commit that introduced a bug:
git bisect start
git bisect bad
git bisect good <commit-id>
8. Reverse List
Reverses the order of commits in a log:
git log --reverse
9. Filter Branch
Used to rewrite the history of a repository:
git filter-branch --tree-filter 'rm -f <file>' -- <branch-name>
10. Cherry Pick
Applies the changes from a specific commit to the current branch:
git cherry-pick <commit-id>
11. GitHub
GPG Usage
Sign commits with GPG for added security:
git commit -S -m "Signed commit"
LICENSE
GitHub supports various licenses. A common license is MIT, which you can add by creating a LICENSE file in the root of your repository.
Teamwork
GitHub makes it easy to collaborate on projects. You can create teams, set permissions, and manage pull requests.
12. GitHub CLI Tool
The GitHub CLI allows you to manage GitHub repositories from the command line:
gh repo create
gh pr create
gh issue create
13. GitHub Wiki
You can enable a wiki in a GitHub repository to document your project. Access it via the "Wiki" tab on your repository's GitHub page.
14. Shorten GitHub URL
Use GitHub Shortener to shorten URLs.
15. GitHub Flavored Markdown
GitHub uses a slightly different flavor of Markdown. For more details, refer to GitHub Flavored Markdown.
16. GitHub Pages
GitHub Pages allows you to host static websites directly from your GitHub repository.
17. GitHub Git Attributes
Define how Git should treat files with .gitattributes.
*.jpg binary
18. GitHub Actions
Automate your workflow using GitHub Actions. Set up CI/CD pipelines.
19. GitHub Dependabot
GitHub Dependabot automatically keeps your dependencies up-to-date by submitting pull requests for outdated dependencies.
20. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot assists with code completion and suggestions inside your editor.
21. Git Internals
Git Objects
Git stores data as objects. The main objects are:
- Commit: A snapshot of the project at a point in time.
- Tree: A directory of files.
- Blob: A file's contents.
- Tag: A reference to a commit.
Git Packfiles
Git uses packfiles to store objects efficiently, allowing the repository to grow without consuming excessive space.
22. Git Inside Commands
These commands reflect the internal workings of Git:
Add Inside
git add <file-name>
Commit Inside
git commit -m "Commit message"
Checkout Inside
git checkout <branch-name>
Merge Inside
git merge <branch-name>
Fetch Inside
git fetch <remote>
Clone Inside
git clone <repository-url>
Push Inside
git push <remote> <branch-name>
Branch Inside
Git Resources
Here are some helpful resources to understand and work with Git:
- Git repository
- Explain Git with D3 - A visual guide to understand Git concepts with interactive D3.js graphics.
- Visual Git Guide - A visual guide to common Git commands and workflows.
- Oh My Git! - An interactive Git game that helps you learn Git commands.
- Learn Git Branching - An interactive platform to master Git branching.
- Git and GitHub Learning Resources - Official GitHub documentation and tutorials to help you get started with Git and GitHub.